Introduction
UN Peacekeeping helps countries to achieve lasting peace, supports political processes, protects hundreds of thousands of civilians and helps guarantee cease fires. Yet peacekeeping faces several challenges such as protracted conflicts, elusive political solutions, increasingly dangerous environments, rising peacekeeping fatalities, and broad and complex mandates. To respond to these challenges, the Secretary-General launched Action for Peacekeeping (A4P) to refocus peacekeeping with more targeted mandates, make our operations stronger and safer, mobilize support for political solutions and better equipped and trained forces. A4P represents the core agenda for our action and is a driver of change permeating all aspects of UN's peacekeeping work.
Additional information can be obtained on the UN Peacekeeping website.

United Nations Secretary-General
Eight areas of Improvement
The A4P initiative aims to strengthen peacekeeping by spurring collective action by all peacekeeping stakeholders, including all Member States, the Security Council, the General Assembly, financial contributors, troop and police contributing countries, host countries, intergovernmental and regional organizations and the UN Secretariat. We will achieve these goals through the implementation of a set of 45 mutually-agreed commitments that were endorsed by more than 150 Member States across 8 areas.
The Road to Implementation
All peacekeeping stakeholders have a responsibility to strengthen peacekeeping. The A4P Declaration details 45 specific commitments. Some are from the UN Secretary-General on behalf of UN missions and the Secretariat; some are from Member States, on behalf of the Security Council, troop- and police- contributors, as well as host governments; others are of a collective nature. The UN Secretariat is progressing in fulfilling its commitments as outlined below. Member States are encouraged to support A4P by focusing on their commitments and working with the UN Secretariat on collective items.
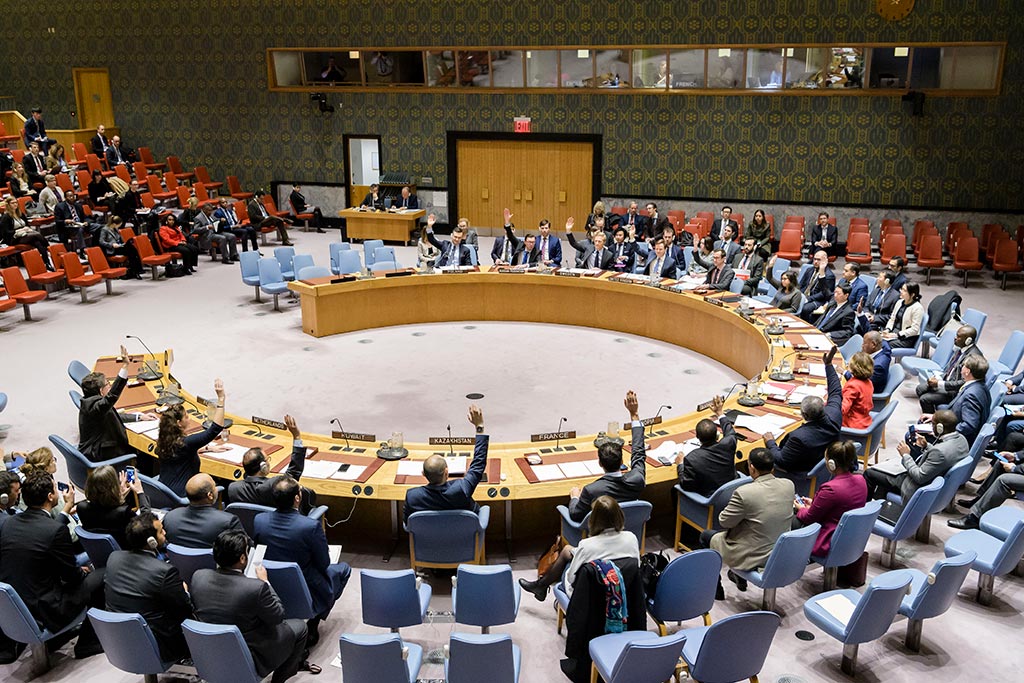


Advance political solutions to conflict and enhance the political impact of peacekeeping
We collectively commit to stronger engagement to advance political solutions to conflict and to pursue complementary political objectives and integrated strategies, including at national and regional levels, within our respective mandates and responsibilities. We affirm that the pursuit of sustainable political solutions should guide the design and deployment of UN peacekeeping operations. We recognize that lasting progress in strengthening security, national reconciliation, the rule of law, human rights and sustainable development needs to occur in parallel.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are developing country and regional political strategies to make our missions fit for purpose, including through analysis, data and approaches coordinated across the peace and security pillar, with a priority on prevention and sustaining peace. Read more about politics
Photo: A wide view of the Security Council meeting as it unanimously adopts resolution 2450 (2018), renewing the mandate of the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force (UNDOF) for a period of six months, until 30 June 2019. UN Photo/Manuel Elias
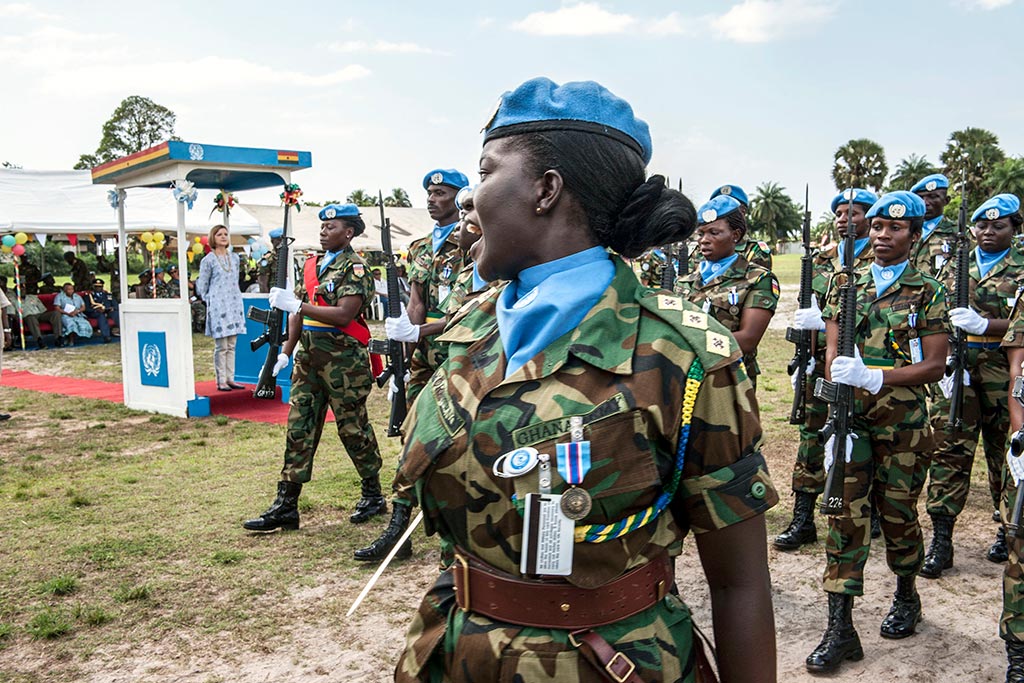

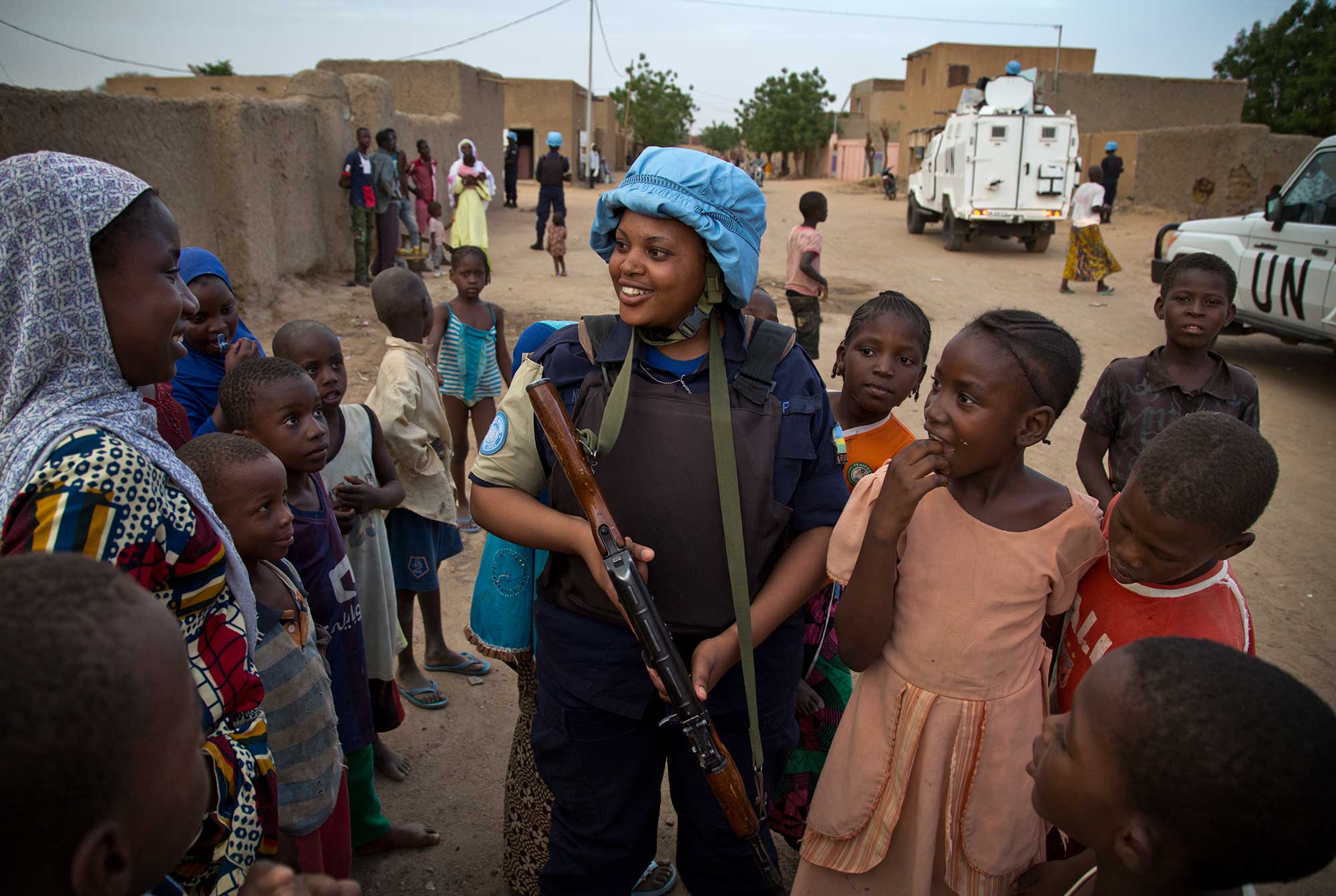
Implement the women, peace and security agenda
We collectively commit to implement the Women, Peace and Security agenda and its priorities by ensuring full, equal and meaningful participation of women in all stages of the peace process and by systematically integrating a gender perspective into all stages of analysis, planning, implementation and reporting. We further recommit to increasing the number of civilian and uniformed women in peacekeeping at all levels and in key positions.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are taking steps towards the full, equal and meaningful participation of women in peace processes and peacekeeping operations in order to make peace sustainable. Read more about women, peace and security
Photo: UNMIL Special Representative Karin Landgren reviews Ghanaian peacekeepers during a medal parade in Buchanan, Liberia, Friday, in 2012. UNMIL Photo/Staton Winter
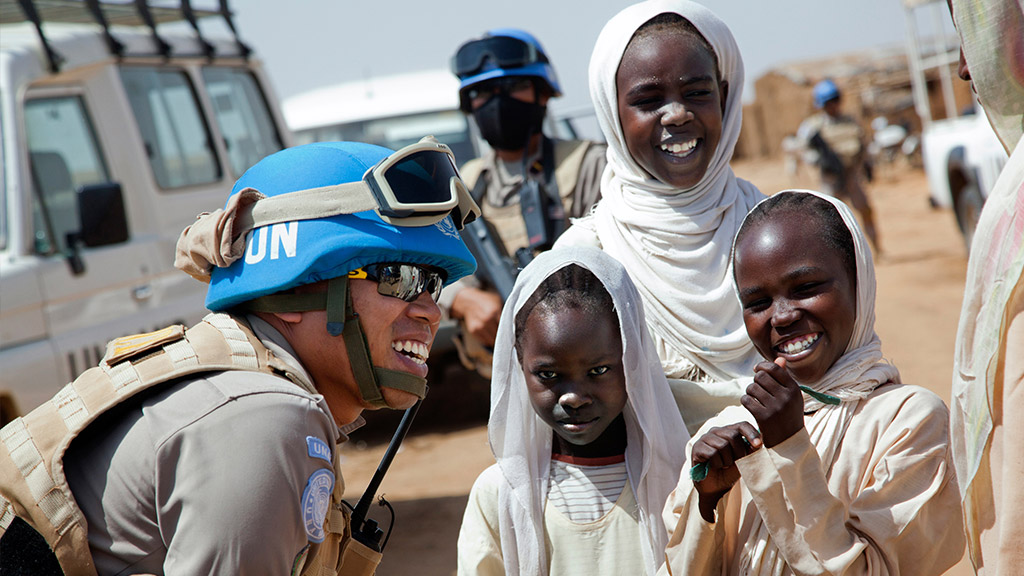



Strengthen the protection provided by peacekeeping operations
We collectively commit to support tailored, context-specific peacekeeping approaches to protecting civilians, in relevant peacekeeping operations, emphasising the protection of women and children in those contexts. We commit to implement protection of civilians mandates of peacekeeping missions, including through using all necessary means when required, in accordance with the UN Charter, mission mandates, and applicable international law. We further commit to improving strategic communications and engagement with local populations to strengthen the understanding of the peacekeeping missions and their mandates.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are putting strategic approaches to protection at the heart of mission actions; we are assessing more vigorously our military units on protection and are strengthening coordinated approaches to community engagement in order to prevent, mitigate and respond more effectively to threats. Read more about protection
Photo: UNAMID peacekeeper Lieutenant Colonel Yenni Windarti, of the Indonesia's civilian police, interacts with women and children at a water point in Abu Shouk camp for Internally Displaced Persons (North Darfur) during a morning patrol. UN Photo/Albert González Farran
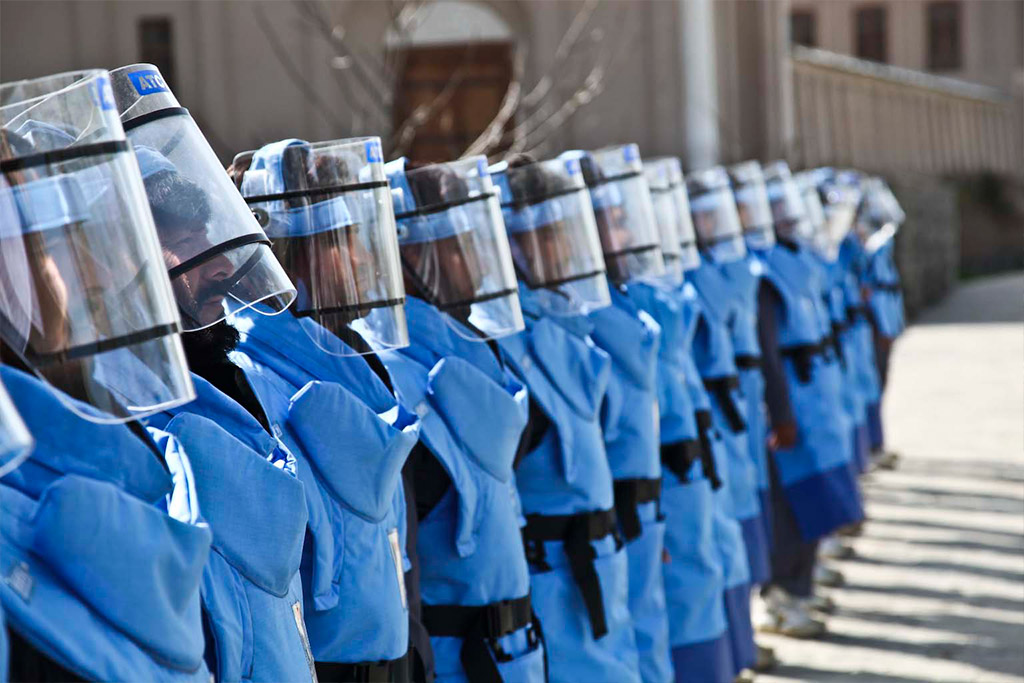

Improve the safety and security of peacekeepers
Recognizing the evolving challenges in today’s conflict environments, we collectively commit to take active and concerted measures to address the rise in peacekeeper fatalities and enhance safety and security, and in this regard, we note the importance of the Secretary-General’s Action Plan and Peacekeeping Training Plan, as well as efforts to improve continually medical, technical and logistical support in peacekeeping operations.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are implementing the Action Plan to Improve the Security of Peacekeepers that focuses on changing mindsets, improving capacities such as casualty and medical evacuations and use of technology, achieving a threat sensitive footprint and enhancing accountability in order to bring perpetrators of crimes against peacekeepers to justice. Read more about safety and security
Photo: Landmine removal makes it possible for peacekeepers to carry out patrols, for humanitarian agencies to deliver assistance, and for ordinary citizens to live without the fear that a single misstep could cost them their lives. In Afghanistan, over 14,000 Afghans are employed in the mine action sector. UN Photo/UNAMA
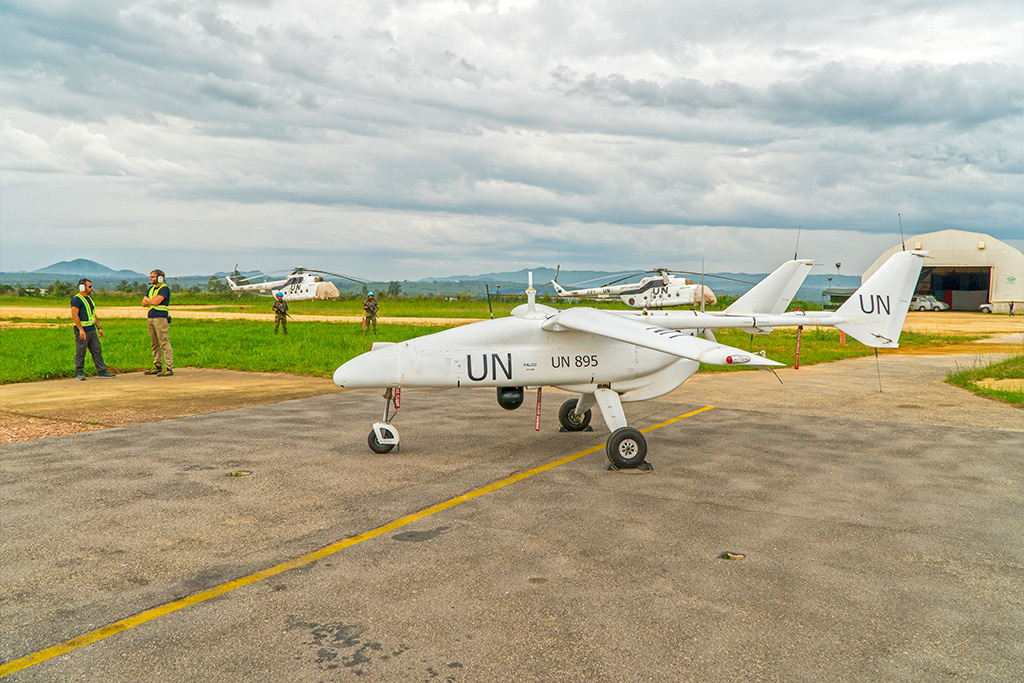



Support effective performance and accountability by all peacekeeping components
We collectively commit to ensuring the highest level of peacekeeping performance, and to hold all civilian and uniformed peacekeepers, particularly leadership, accountable for effective performance under common parameters while addressing performance shortfalls. The Secretary-General commits to develop an integrated performance policy framework based on clear standards for all actors, and to ensure that performance data is used to inform planning, evaluation, deployment decisions and reporting; to communicate to Member States all operational and technical requirements; to provide effective field support to peacekeeping operations, and to work with Member States to generate the necessary specialized capabilities, including language skills, while supporting new approaches to improve force generation, equipment serviceability and sustainability.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are developing an integrated performance policy framework and rolling out the Comprehensive Performance Assessment System which will help track performance and strengthen accountability; in the context of the Action Plan to Improve the Security of Peacekeepers, we are verifying the operational readiness of troops and police and engaging more actively with troops and police contributors on performance. Read more about performance and accountability
Photo: A UUAV fuels up before taking off on a reconnaissance flight in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Starting with the DRC in 2013, several missions have employed unarmed and unmanned aerial vehicles (UUAVs). The UUAVs provide real-time visuals of situations as they develop on the ground. By improving response times, the UUAVs allow the UN to better protect civilians. UUAVs can also warn of impending attacks against peacekeepers. UN Photo/Sylvain Liechti
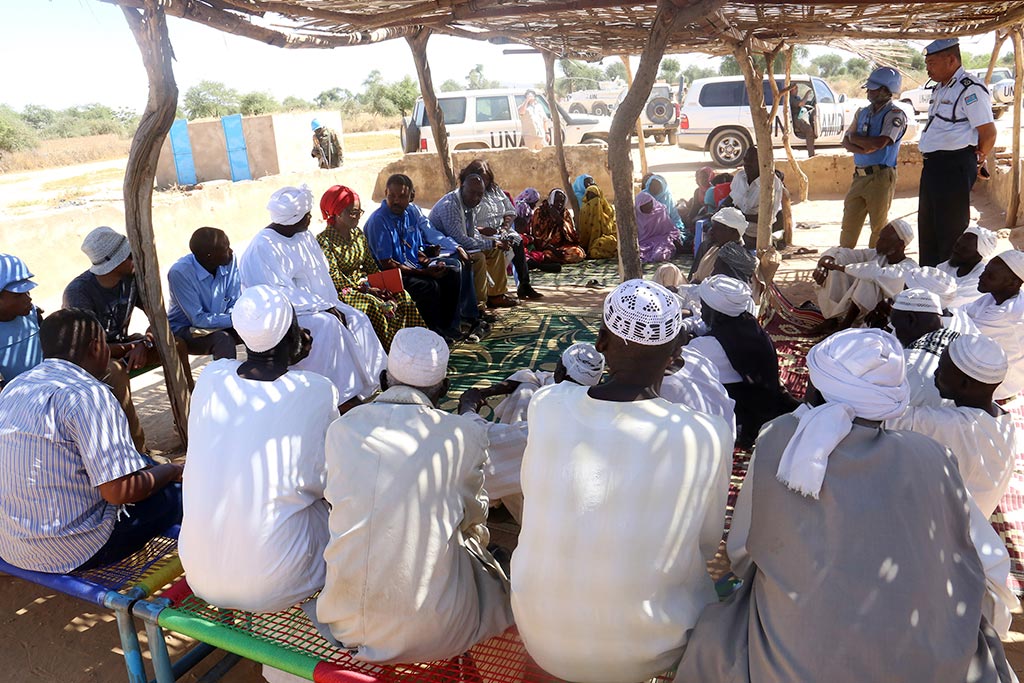

Strengthen the impact of peacekeeping on sustaining peace
We collectively commit to support inclusive and participatory approaches by peacekeeping operations with the host government. We further support the inclusion and engagement of civil society and all segments of the local population in peacekeeping mandate implementation. We further commit to strong coordination, coherence and cooperation between the Security Council and the Peacebuilding Commission during peacekeeping mandates, as appropriate. During transitions from peacekeeping operations, we commit to support UN Country Teams to continue assisting host countries to build peace.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are strengthening our partnerships with peacebuilding stakeholders (e.g. UN/World Bank partnership), we are developing comprehensive transition and resource mobilization strategies for Haiti and Darfur, and strengthening the Global Focal Point for Justice and Rule of Law. Read more about peacebuilding and sustaining peace
Photo: UNAMID Deputy Joint Special Representative, Ms. Anita Kiki Gbeho, visits Rongatas IDP camp, in Central Darfur. She briefs the representatives of displaced people on the Mission’s ongoing reconfiguration and listens to their security and humanitarian concerns. UN Photo/Mohammed Idriss
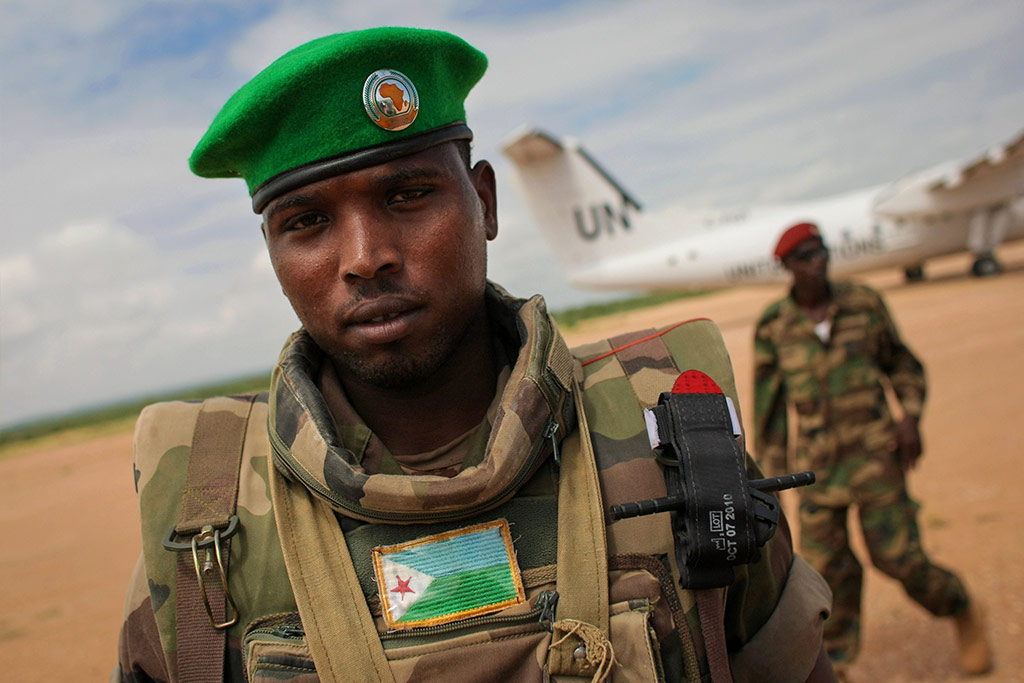



Improve peacekeeping partnerships to enhance collaboration and planning
We collectively commit to enhance collaboration and planning between the UN and relevant international, regional and sub-regional organizations and arrangements, including the African Union (AU) and the European Union (EU), which have deployed several mandated operations in the past years, while recognising the need for a clear delineation of roles between respective operations. We commit to support the AU to strengthen and implement its policies, procedures and capacities, including on compliance. Recognising the Security Council’s primary responsibility for the maintenance of international peace and security, we reaffirm the need to enhance the predictability, sustainability and flexibility of financing for AU-led peace support operations authorized by the Security Council, and under the Security Council’s authority consistent with Chapter VIII of the UN Charter.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are strengthening the UN/African Union cooperation on political efforts, including via joint field visits and joint consultative mechanisms, as well as bolstering AU peace operations capacity. To address other aspects of partnerships, we are expanding the Triangular Partnership Project, which builds long-term capacity for troop contributors and allows financial contributors to flexibly support enabling capacity such as engineering and medical. Read more about partnerships
Photo: A soldier of the Djiboutian Contingent serving with the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) stands guard as a United Nations aircraft prepares for take-off from Belet Weyne Airport. AU PHOTO/Stuart Price
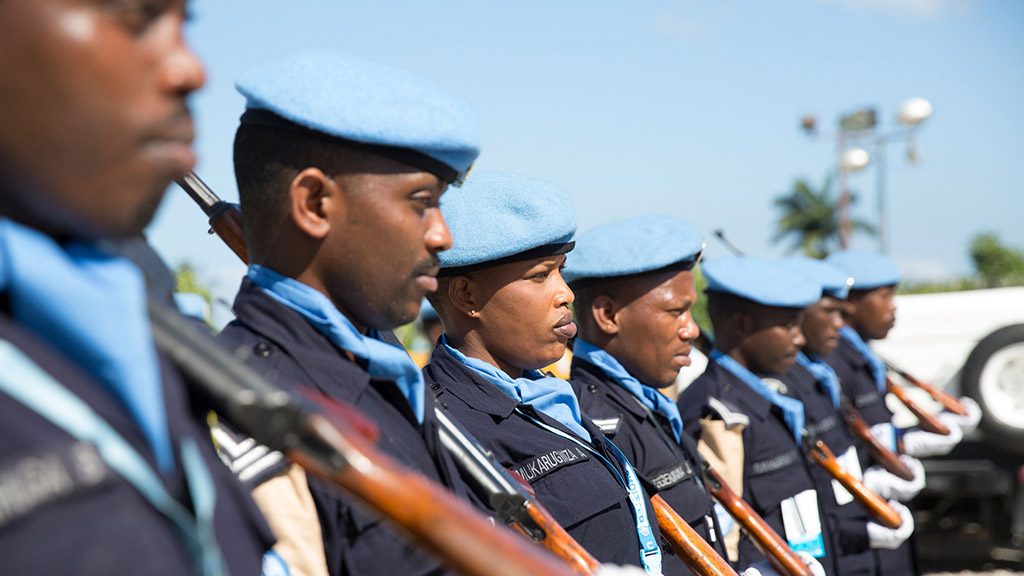

Strengthen conduct of peacekeeping operations and personnel
We collectively commit, within our respective responsibilities, to holding personnel and leadership accountable for proper conduct, including through support to the UN zero-tolerance policy with its victim-centred approach on all forms of sexual exploitation and abuse. We commit as Member States to certifying that prospective personnel meet UN standards for service in UN peacekeeping operations.
To fulfil the Secretariat’s commitments, we are urging all Member States to sign the Voluntary Compact on the commitment to eliminate sexual exploitation and abuse. To address other aspects of the conduct of peacekeeping operations, we are strengthening the implementation of our Human Rights Due Diligence Policy as well as our Environment Strategy which aims to reduce our footprint in the field. Read more about conduct of peacekeepers and peacekeeping operations
Photo: A Formed Police Unit from Rwanda serving with MINUJUSTH in Haiti stands at attention. UN Photo/Leonora Bauman

More than 150 endorsements
The Declaration of Shared Commitments has reached over 150 endorsements and provides a shared roadmap for strengthening peacekeeping. Success depends on Member States and the UN Secretariat working actively to implement their shared commitments.
“We as endorsers of this Declaration commit to translating these commitments into our positions and practices in the relevant UN bodies, including the General Assembly and the Security Council in their consideration of peacekeeping, and to meet periodically in relevant formats to review progress, including at field-level.”
The following organisations support the A4P Declaration: European Union (EU), Organisation internationale de la francophonie (OIF), African Union Commission (AU), and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
Additional information, including updates on implementation and official statements of support for the A4P initiative can be obtained on the UN Peacekeeping website.